#include <stdbool.h>#include <stddef.h>#include "rcl/client.h"#include "rcl/guard_condition.h"#include "rcl/macros.h"#include "rcl/service.h"#include "rcl/subscription.h"#include "rcl/timer.h"#include "rcl/types.h"#include "rcl/visibility_control.h"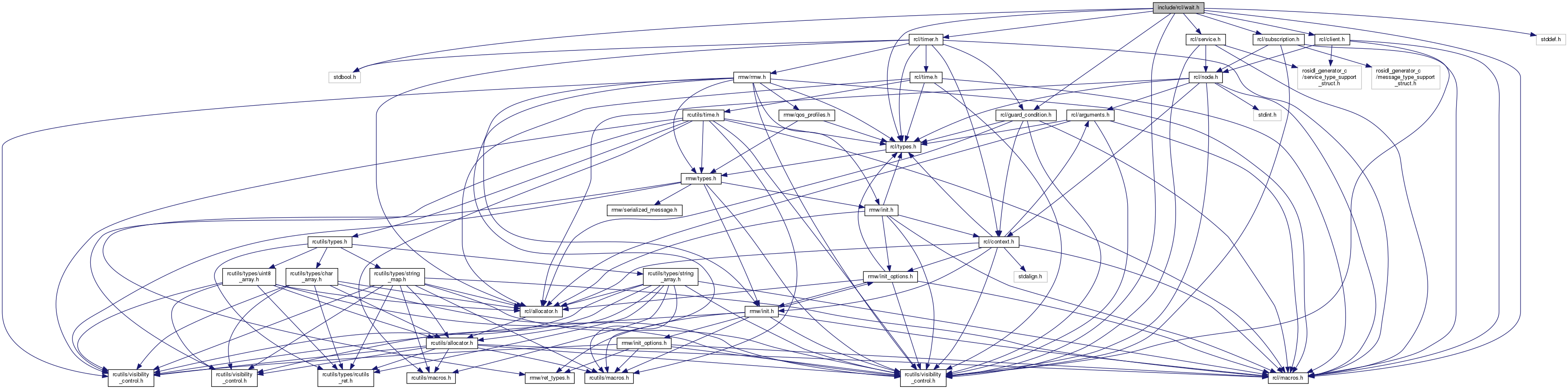
Go to the source code of this file.
Classes | |
| struct | rcl_wait_set_t |
| Container for subscription's, guard condition's, etc to be waited on. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef struct rcl_wait_set_t | rcl_wait_set_t |
| Container for subscription's, guard condition's, etc to be waited on. More... | |
Functions | |
| rcl_wait_set_t | rcl_get_zero_initialized_wait_set (void) |
Return a rcl_wait_set_t struct with members set to NULL. More... | |
| rcl_ret_t | rcl_wait_set_init (rcl_wait_set_t *wait_set, size_t number_of_subscriptions, size_t number_of_guard_conditions, size_t number_of_timers, size_t number_of_clients, size_t number_of_services, rcl_allocator_t allocator) |
| Initialize a rcl wait set with space for items to be waited on. More... | |
| rcl_ret_t | rcl_wait_set_fini (rcl_wait_set_t *wait_set) |
| Finalize a rcl wait set. More... | |
| rcl_ret_t | rcl_wait_set_get_allocator (const rcl_wait_set_t *wait_set, rcl_allocator_t *allocator) |
| Retrieve the wait set's allocator. More... | |
| rcl_ret_t | rcl_wait_set_add_subscription (rcl_wait_set_t *wait_set, const rcl_subscription_t *subscription, size_t *index) |
| Store a pointer to the given subscription in the next empty spot in the set. More... | |
| rcl_ret_t | rcl_wait_set_clear (rcl_wait_set_t *wait_set) |
Remove (sets to NULL) all entities in the wait set. More... | |
| rcl_ret_t | rcl_wait_set_resize (rcl_wait_set_t *wait_set, size_t subscriptions_size, size_t guard_conditions_size, size_t timers_size, size_t clients_size, size_t services_size) |
| Reallocate space for entities in the wait set. More... | |
| rcl_ret_t | rcl_wait_set_add_guard_condition (rcl_wait_set_t *wait_set, const rcl_guard_condition_t *guard_condition, size_t *index) |
| Store a pointer to the guard condition in the next empty spot in the set. More... | |
| rcl_ret_t | rcl_wait_set_add_timer (rcl_wait_set_t *wait_set, const rcl_timer_t *timer, size_t *index) |
| Store a pointer to the timer in the next empty spot in the set. More... | |
| rcl_ret_t | rcl_wait_set_add_client (rcl_wait_set_t *wait_set, const rcl_client_t *client, size_t *index) |
| Store a pointer to the client in the next empty spot in the set. More... | |
| rcl_ret_t | rcl_wait_set_add_service (rcl_wait_set_t *wait_set, const rcl_service_t *service, size_t *index) |
| Store a pointer to the service in the next empty spot in the set. More... | |
| rcl_ret_t | rcl_wait (rcl_wait_set_t *wait_set, int64_t timeout) |
| Block until the wait set is ready or until the timeout has been exceeded. More... | |
Typedef Documentation
◆ rcl_wait_set_t
| typedef struct rcl_wait_set_t rcl_wait_set_t |
Container for subscription's, guard condition's, etc to be waited on.
Function Documentation
◆ rcl_get_zero_initialized_wait_set()
| rcl_wait_set_t rcl_get_zero_initialized_wait_set | ( | void | ) |
Return a rcl_wait_set_t struct with members set to NULL.
◆ rcl_wait_set_init()
| rcl_ret_t rcl_wait_set_init | ( | rcl_wait_set_t * | wait_set, |
| size_t | number_of_subscriptions, | ||
| size_t | number_of_guard_conditions, | ||
| size_t | number_of_timers, | ||
| size_t | number_of_clients, | ||
| size_t | number_of_services, | ||
| rcl_allocator_t | allocator | ||
| ) |
Initialize a rcl wait set with space for items to be waited on.
This function allocates space for the subscriptions and other wait-able entities that can be stored in the wait set. It also sets the allocator to the given allocator and initializes the pruned member to be false.
The wait_set struct should be allocated and initialized to NULL. If the wait_set is allocated but the memory is uninitialized the behavior is undefined. Calling this function on a wait set that has already been initialized will result in an error. A wait set can be reinitialized if rcl_wait_set_fini() was called on it.
To use the default allocator use rcl_get_default_allocator().
Expected usage:
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Yes |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in,out] wait_set the wait set struct to be initialized [in] number_of_subscriptions non-zero size of the subscriptions set [in] number_of_guard_conditions non-zero size of the guard conditions set [in] number_of_timers non-zero size of the timers set [in] number_of_clients non-zero size of the clients set [in] number_of_services non-zero size of the services set [in] allocator the allocator to use when allocating space in the sets
- Returns
RCL_RET_OKif the wait set is initialized successfully, or-
RCL_RET_ALREADY_INITif the wait set is not zero initialized, or -
RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENTif any arguments are invalid, or -
RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOCif allocating memory failed, or -
RCL_RET_ERRORif an unspecified error occurs.
◆ rcl_wait_set_fini()
| rcl_ret_t rcl_wait_set_fini | ( | rcl_wait_set_t * | wait_set | ) |
Finalize a rcl wait set.
Deallocates any memory in the wait set that was allocated in rcl_wait_set_init() using the allocator given in the initialization.
Calling this function on a zero initialized wait set will do nothing and return RCL_RET_OK. Calling this function on uninitialized memory results in undefined behavior. After calling this function the wait set will once again be zero initialized and so calling this function or rcl_wait_set_init() immediately after will succeed.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Yes |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in,out] wait_set the wait set struct to be finalized.
- Returns
RCL_RET_OKif the finalization was successful, or-
RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENTif any arguments are invalid, or -
RCL_RET_ERRORif an unspecified error occurs.
◆ rcl_wait_set_get_allocator()
| rcl_ret_t rcl_wait_set_get_allocator | ( | const rcl_wait_set_t * | wait_set, |
| rcl_allocator_t * | allocator | ||
| ) |
Retrieve the wait set's allocator.
The allocator must be an allocated rcl_allocator_t struct, as the result is copied into this variable.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Yes |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in] wait_set the handle to the wait set [out] allocator the rcl_allocator_t struct to which the result is copied
- Returns
RCL_RET_OKif the allocator was successfully retrieved, or-
RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENTif any arguments are invalid, or -
RCL_RET_ERRORif an unspecified error occurs.
◆ rcl_wait_set_add_subscription()
| rcl_ret_t rcl_wait_set_add_subscription | ( | rcl_wait_set_t * | wait_set, |
| const rcl_subscription_t * | subscription, | ||
| size_t * | index | ||
| ) |
Store a pointer to the given subscription in the next empty spot in the set.
This function does not guarantee that the subscription is not already in the wait set.
Also add the rmw representation to the underlying rmw array and increment the rmw array count.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Yes |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in,out] wait_set struct in which the subscription is to be stored [in] subscription the subscription to be added to the wait set [out] index the index of the added subscription in the storage container. This parameter is optional and can be set to NULLto be ignored.
- Returns
RCL_RET_OKif added successfully, or-
RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENTif any arguments are invalid, or -
RCL_RET_WAIT_SET_INVALIDif the wait set is zero initialized, or -
RCL_RET_WAIT_SET_FULLif the subscription set is full, or -
RCL_RET_ERRORif an unspecified error occurs.
◆ rcl_wait_set_clear()
| rcl_ret_t rcl_wait_set_clear | ( | rcl_wait_set_t * | wait_set | ) |
Remove (sets to NULL) all entities in the wait set.
This function should be used after passing using rcl_wait, but before adding new entities to the set. Sets all of the entries in the underlying rmw array to NULL, and sets the count in the rmw array to 0.
Calling this on an uninitialized (zero initialized) wait set will fail.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in,out] wait_set struct to have its entities cleared
- Returns
RCL_RET_OKif cleared successfully, or-
RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENTif any arguments are invalid, or -
RCL_RET_WAIT_SET_INVALIDif the wait set is zero initialized, or -
RCL_RET_ERRORif an unspecified error occurs.
◆ rcl_wait_set_resize()
| rcl_ret_t rcl_wait_set_resize | ( | rcl_wait_set_t * | wait_set, |
| size_t | subscriptions_size, | ||
| size_t | guard_conditions_size, | ||
| size_t | timers_size, | ||
| size_t | clients_size, | ||
| size_t | services_size | ||
| ) |
Reallocate space for entities in the wait set.
This function will deallocate and reallocate the memory for all entity sets.
A size of 0 will just deallocate the memory and assign NULL to the array.
Allocation and deallocation is done with the allocator given during the wait set's initialization.
After calling this function all values in the set will be set to NULL, effectively the same as calling rcl_wait_set_clear(). Similarly, the underlying rmw representation is reallocated and reset: all entries are set to NULL and the count is set to zero.
If the requested size matches the current size, no allocation will be done.
This can be called on an uninitialized (zero initialized) wait set.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Yes |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in,out] wait_set struct to be resized [in] subscriptions_size a size for the new subscriptions set [in] guard_conditions_size a size for the new guard conditions set [in] timers_size a size for the new timers set [in] clients_size a size for the new clients set [in] services_size a size for the new services set
- Returns
RCL_RET_OKif resized successfully, or-
RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENTif any arguments are invalid, or -
RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOCif allocating memory failed, or -
RCL_RET_ERRORif an unspecified error occurs.
◆ rcl_wait_set_add_guard_condition()
| rcl_ret_t rcl_wait_set_add_guard_condition | ( | rcl_wait_set_t * | wait_set, |
| const rcl_guard_condition_t * | guard_condition, | ||
| size_t * | index | ||
| ) |
Store a pointer to the guard condition in the next empty spot in the set.
This function behaves exactly the same as for subscriptions.
- See also
- rcl_wait_set_add_subscription
◆ rcl_wait_set_add_timer()
| rcl_ret_t rcl_wait_set_add_timer | ( | rcl_wait_set_t * | wait_set, |
| const rcl_timer_t * | timer, | ||
| size_t * | index | ||
| ) |
Store a pointer to the timer in the next empty spot in the set.
This function behaves exactly the same as for subscriptions.
- See also
- rcl_wait_set_add_subscription
◆ rcl_wait_set_add_client()
| rcl_ret_t rcl_wait_set_add_client | ( | rcl_wait_set_t * | wait_set, |
| const rcl_client_t * | client, | ||
| size_t * | index | ||
| ) |
Store a pointer to the client in the next empty spot in the set.
This function behaves exactly the same as for subscriptions.
- See also
- rcl_wait_set_add_subscription
◆ rcl_wait_set_add_service()
| rcl_ret_t rcl_wait_set_add_service | ( | rcl_wait_set_t * | wait_set, |
| const rcl_service_t * | service, | ||
| size_t * | index | ||
| ) |
Store a pointer to the service in the next empty spot in the set.
This function behaves exactly the same as for subscriptions.
- See also
- rcl_wait_set_add_subscription
◆ rcl_wait()
| rcl_ret_t rcl_wait | ( | rcl_wait_set_t * | wait_set, |
| int64_t | timeout | ||
| ) |
Block until the wait set is ready or until the timeout has been exceeded.
This function will collect the items in the rcl_wait_set_t and pass them to the underlying rmw_wait function.
The items in the wait set will be either left untouched or set to NULL after this function returns. Items that are not NULL are ready, where ready means different things based on the type of the item. For subscriptions this means there may be messages that can be taken, or perhaps that the state of the subscriptions has changed, in which case rcl_take may succeed but return with taken == false. For guard conditions this means the guard condition was triggered.
Expected usage:
The wait set struct must be allocated, initialized, and should have been cleared and then filled with items, e.g. subscriptions and guard conditions. Passing a wait set with no wait-able items in it will fail. NULL items in the sets are ignored, e.g. it is valid to have as input:
subscriptions[0]= valid pointersubscriptions[1]=NULLsubscriptions[2]= valid pointersize_of_subscriptions= 3 Passing an uninitialized (zero initialized) wait set struct will fail. Passing a wait set struct with uninitialized memory is undefined behavior.
The unit of timeout is nanoseconds. If the timeout is negative then this function will block indefinitely until something in the wait set is valid or it is interrupted. If the timeout is 0 then this function will be non-blocking; checking what's ready now, but not waiting if nothing is ready yet. If the timeout is greater than 0 then this function will return after that period of time has elapsed or the wait set becomes ready, which ever comes first. Passing a timeout struct with uninitialized memory is undefined behavior.
This function is thread-safe for unique wait sets with unique contents. This function cannot operate on the same wait set in multiple threads, and the wait sets may not share content. For example, calling rcl_wait() in two threads on two different wait sets that both contain a single, shared guard condition is undefined behavior.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] wait_set the set of things to be waited on and to be pruned if not ready [in] timeout the duration to wait for the wait set to be ready, in nanoseconds
- Returns
RCL_RET_OKsomething in the wait set became ready, or-
RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENTif any arguments are invalid, or -
RCL_RET_WAIT_SET_INVALIDif the wait set is zero initialized, or -
RCL_RET_WAIT_SET_EMPTYif the wait set contains no items, or -
RCL_RET_TIMEOUTif the timeout expired before something was ready, or -
RCL_RET_ERRORan unspecified error occur.
 1.8.13
1.8.13